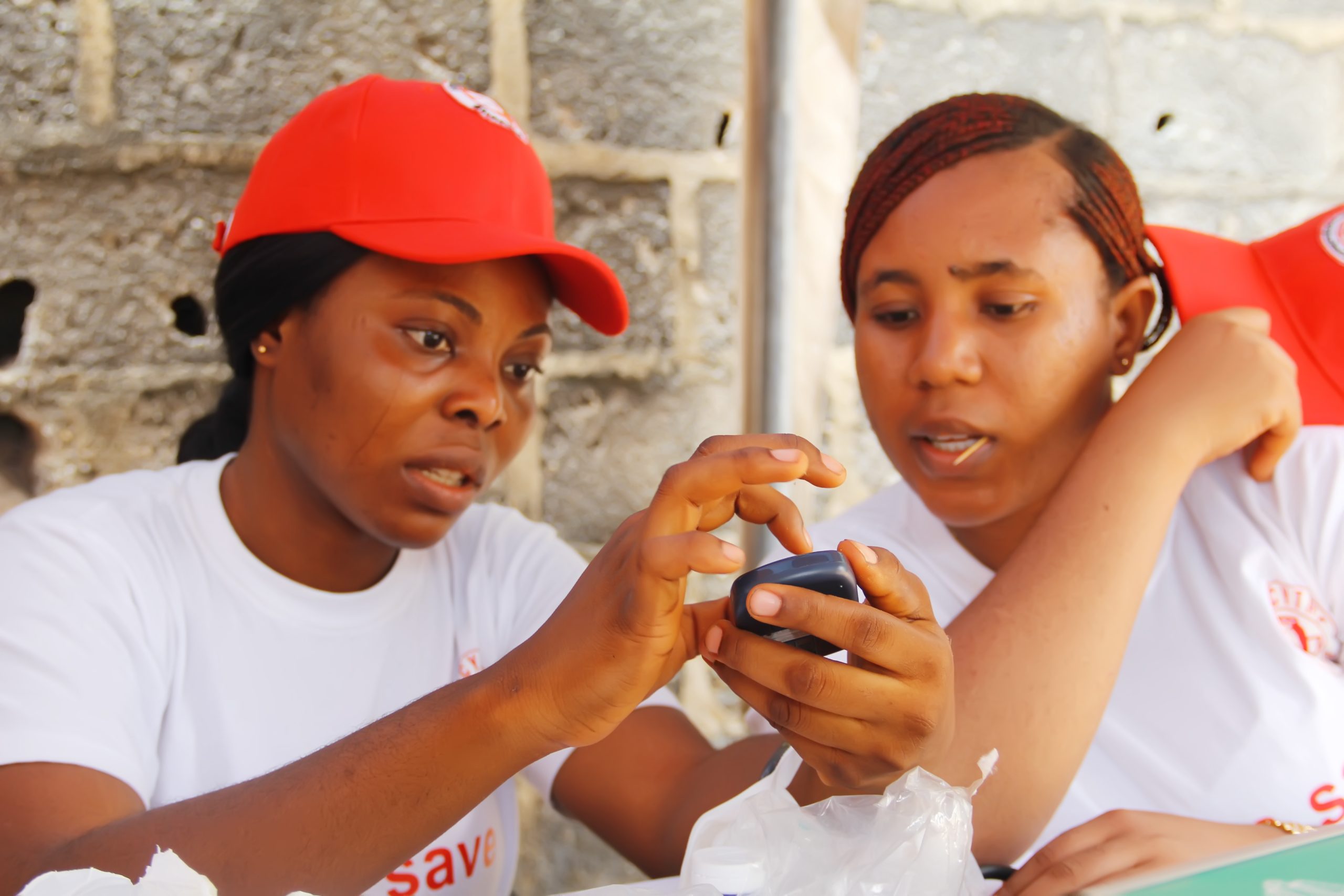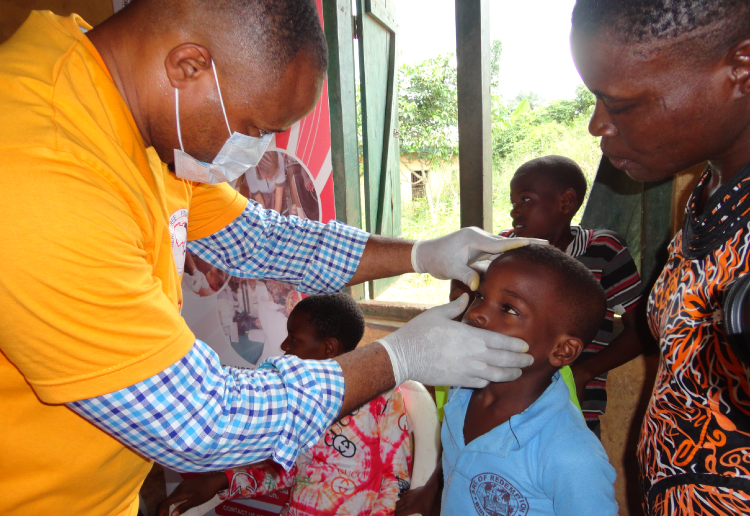
Hepatitis is a serious inflammation of the liver, most commonly caused by viral infections (Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E). Each type carries its own risk factors, yet all can lead to severe complications such as liver failure, cirrhosis, or liver cancer if untreated. Hepatitis B and C, in particular, are silent killers, often showing no symptoms until the disease has advanced. According to global health statistics, millions of people are infected each year, with Sub-Saharan Africa bearing a heavy burden due to lack of awareness, preventive measures, and access to early testing.
Statement of Need: Health Effects and Community Impact
The impact of hepatitis extends far beyond the individual—it destabilizes families, strains already fragile healthcare systems, and erodes community well-being. Children are at risk of mother-to-child transmission, while adults face stigma and discrimination that hinders treatment-seeking behavior. The economic consequences include loss of productivity, rising healthcare costs, and premature deaths, all of which trap vulnerable communities in cycles of poverty and illness. Without urgent intervention, hepatitis will continue to silently devastate communities.
Urgency of the Situation
Hepatitis does not wait. The longer the delay in diagnosis, education, and treatment, the greater the spread and the higher the fatality rates. Unlike other diseases, the lack of visible early symptoms makes hepatitis even more dangerous, creating an invisible epidemic. The need for urgent awareness, vaccination campaigns, and affordable screening cannot be overstated. Without immediate action, countless lives—particularly among children and young adults—will remain at risk.
Limited Medical and Personnel Resources
In many underserved communities, there are few or no facilities equipped to diagnose and manage hepatitis effectively. Medical staff are overstretched, lacking proper training or diagnostic kits. Laboratories are scarce, vaccines and antiviral medications are often unavailable, and many rural populations have no access to routine screenings. This shortage of trained personnel and resources leaves communities vulnerable, with hepatitis spreading undetected.
Challenges Faced by Stakeholders
- Health Workers struggle with insufficient diagnostic tools, lack of training, and limited access to vaccines and treatment options.
- Community Members face stigma, myths, and misinformation, leading to fear and reluctance to seek help.
- Families bear emotional and financial burdens from chronic illness and loss of income when caregivers or breadwinners are affected.
- Policy Makers and Partners encounter competing priorities, which limit budget allocations and sustainable responses to hepatitis.
MercyTree Foundation’s Program Initiatives
To combat this silent epidemic, MercyTree Foundation has launched the Hepatitis Awareness Initiative with targeted, life-saving interventions:
- Community Awareness Campaigns: Educating communities through workshops, radio programs, and school outreach on hepatitis prevention, transmission, and treatment options.
- Free Screening Days: Organizing regular community-based testing to detect hepatitis early and link patients to care.
- Vaccination Drives: Ensuring children and at-risk adults receive hepatitis vaccines, reducing mother-to-child transmission and community spread.
- Training for Health Workers: Equipping frontline healthcare providers with knowledge and resources to diagnose, counsel, and treat patients effectively.
- Support Networks: Establishing peer-support groups for patients and families, reducing stigma and encouraging treatment adherence.
- Advocacy and Partnerships: Collaborating with government, NGOs, and international partners to strengthen policies, secure resources, and integrate hepatitis programs into broader health systems.
Through this initiative, MercyTree Foundation is bringing hope, protection, and healing to vulnerable communities, breaking the silence around hepatitis, and paving the way for healthier generations.
- Description
-
Hepatitis is a serious inflammation of the liver, most commonly caused by viral infections (Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E). Each type carries its own risk factors, yet all can lead to severe complications such as liver failure, cirrhosis, or liver cancer if untreated. Hepatitis B and C, in particular, are silent killers, often showing no symptoms until the disease has advanced. According to global health statistics, millions of people are infected each year, with Sub-Saharan Africa bearing a heavy burden due to lack of awareness, preventive measures, and access to early testing.
Statement of Need: Health Effects and Community Impact
The impact of hepatitis extends far beyond the individual—it destabilizes families, strains already fragile healthcare systems, and erodes community well-being. Children are at risk of mother-to-child transmission, while adults face stigma and discrimination that hinders treatment-seeking behavior. The economic consequences include loss of productivity, rising healthcare costs, and premature deaths, all of which trap vulnerable communities in cycles of poverty and illness. Without urgent intervention, hepatitis will continue to silently devastate communities.
Urgency of the Situation
Hepatitis does not wait. The longer the delay in diagnosis, education, and treatment, the greater the spread and the higher the fatality rates. Unlike other diseases, the lack of visible early symptoms makes hepatitis even more dangerous, creating an invisible epidemic. The need for urgent awareness, vaccination campaigns, and affordable screening cannot be overstated. Without immediate action, countless lives—particularly among children and young adults—will remain at risk.
Limited Medical and Personnel Resources
In many underserved communities, there are few or no facilities equipped to diagnose and manage hepatitis effectively. Medical staff are overstretched, lacking proper training or diagnostic kits. Laboratories are scarce, vaccines and antiviral medications are often unavailable, and many rural populations have no access to routine screenings. This shortage of trained personnel and resources leaves communities vulnerable, with hepatitis spreading undetected.
Challenges Faced by Stakeholders
- Health Workers struggle with insufficient diagnostic tools, lack of training, and limited access to vaccines and treatment options.
- Community Members face stigma, myths, and misinformation, leading to fear and reluctance to seek help.
- Families bear emotional and financial burdens from chronic illness and loss of income when caregivers or breadwinners are affected.
- Policy Makers and Partners encounter competing priorities, which limit budget allocations and sustainable responses to hepatitis.
MercyTree Foundation’s Program Initiatives
To combat this silent epidemic, MercyTree Foundation has launched the Hepatitis Awareness Initiative with targeted, life-saving interventions:
- Community Awareness Campaigns: Educating communities through workshops, radio programs, and school outreach on hepatitis prevention, transmission, and treatment options.
- Free Screening Days: Organizing regular community-based testing to detect hepatitis early and link patients to care.
- Vaccination Drives: Ensuring children and at-risk adults receive hepatitis vaccines, reducing mother-to-child transmission and community spread.
- Training for Health Workers: Equipping frontline healthcare providers with knowledge and resources to diagnose, counsel, and treat patients effectively.
- Support Networks: Establishing peer-support groups for patients and families, reducing stigma and encouraging treatment adherence.
- Advocacy and Partnerships: Collaborating with government, NGOs, and international partners to strengthen policies, secure resources, and integrate hepatitis programs into broader health systems.
Through this initiative, MercyTree Foundation is bringing hope, protection, and healing to vulnerable communities, breaking the silence around hepatitis, and paving the way for healthier generations.
- Video
-
- Gallery
-
- Donate
-
- Contact Us
-



























